The LRBA (Ballistics and Aeronautical Researches Laboratory) was created in May 1946, within the DEFA (Weapons Studies and Manufactures Directorate). This laboratory, in charge of the study of liquid propellant missiles and the associated ground equipment, undertook since 1948 the realization of a Surface-to-Air weapon system, the Parca (Self-propelled Radio-controlled Projectile Against Planes) which was tested in flight as from 1954.

Veronique
In March 1949, the DEFA decided to build a sounding rocket to allow, at the same time, the in-flight operation study of a liquid powered rocket engine and the upper atmosphere surveys. This rocket (Project 4213), baptized Veronique, was to be as simple and economic as possible. The complete vehicle was to measure 6 m, to weigh a ton at launch, and to be able to send a 60 kg payload to 65 km of altitude. The engine, cooled by double wall propellant circulation, was supplied with nitric acid and kerosene by tanks pressurization. Its 40 kN thrust creating a relatively weak acceleration, it was necessary to conceive a guidance system by unfolding four cables (55 m long) connected at the fins ends. This system was tested using solid rockets, the Veronique P2 and P6, in 1951 and 1952. The first vehicle equipped with the 40 kN liquid engine was the Veronique R (Reduced) of which the burning time had been limited to 6.5 sec instead of nominal 32 sec. It was tested at Suippes range in 1950 and 1951, then at Cardonnet site in early 1952.
The tests of the nominal version, Veronique N, began in 1952 in Hammaguir. Eleven Veronique N were launched there from May 1952 to April 1953, in three series of tests. The failures rate was significant because of low frequency combustion instability problems. In addition, the altitude of 65 km proved to be insufficient to carry out the surveys which interested the atmosphere physicists. It was thus decided to modify the injector to stabilize combustion and to lengthen the tanks to increase the apogee to 135 km with the same 60 kg payload. This version, Veronique NA (Normal Lengthened), was fired four times from Hammaguir between February and October 1954.

The true scientific career of Veronique started when the National Defense Scientific Action Committee subsidized the manufacturing of 15 sounding rockets for the 1957-58 International Geophysical Year (AGI). A new version, named Veronique AGI was born. Although externally similar to Veronique NA, this rocket was lighter and its simplified engine (simple wall) used turpentine in place of kerosene. This new fuel increased the specific impulse and decreased combustion instabilities. While preserving an approximately 40 kN thrust, Veronique AGI could reach 210 km of altitude. The first success was obtained with the second launch in March 1959. As a whole, 48 Veronique AGI were launched from Hammaguir and Kourou between 1959 and 1969, with a 81.5% success ratio.
Since 1961, an increase in the performances of this sounding rocket proved again necessary. Christened Veronique 61, a new version, equipped at once with a 60 kN thrust engine and lengthened tanks, was developed. Capable of carrying a 60 kg payload to 315 km of altitude, its first flight occurred in June 1964. Two years later, it was replaced by a Veronique 61M (Modified) variant, still lengthened and capable of sending up to 100 kg to 325 km of altitude. A total of 22 Veroniques 61 (3 in basic configuration and 19 in 61M version) were launched from Hammaguir and Kourou between 1964 and 1975, with a 90 % success ratio.

Vesta
In second half of the Fifties, the LRBA undertook the study of various concepts for leading
to an improved Veronique, or Super-Veronique. Engines developing 80, 120, 160 and 250 kN were
considered, for rockets intended to send 100 kg payloads at altitudes going from 350 to 600 km
according to the version.
In 1962, the CNES placed order for a new rocket, named Vesta and using a 160 kN engine using
nitric acid and turpentine. Vesta was to measure 10.2 m in length, 1 m in diameter, to weigh 5.1 t
(without payload), and to be capable of sending 500 kg to 400 km of altitude.
After two static firings of the complete vehicle (except the empennage and the nosecone) occurred
in 1964, five Vesta were launched from Hammaguir and Kourou between 1965 and 1969.
Tables
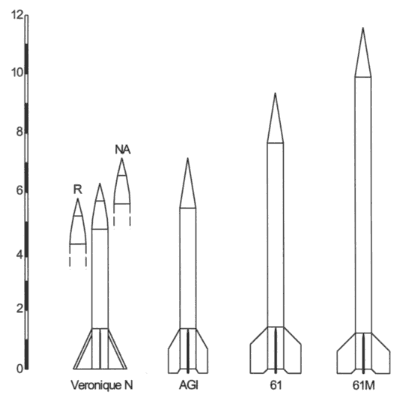
a/ Veronique rockets evolution
b/ Veronique launches
b.1/ preliminary versions
b.2/ operational versions
c/ Vesta launches
Listings with Christophe Rothmund's help (SEP, France)

Scale in meters
| Type | Mass (kg) | Length (m) | Thrust (kN) | Duration (sec) | Payload (kg) | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1100 | 6,5 | 40 | 32 | 60 | 70 |
| NA | 1435 | 7,3 | 40 | 45 | 60 | 135 |
| AGI | 1342 | 7,3 | 40 | 49 | 60 | 210 |
| 61 | 1932 | 9,5 | 60 | 54 | 60 | 315 |
| 61M | 2050 | 11,7 | 60 | 56 | 100 | 325 |
| Date | Site | Vehicle | Mission | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02 Aug 1950 | SPS | Veronique R1 | Technology | S ? (3 m) |
| 05 Aug 1950 | SPS | Veronique R2 | Technology | S ? (8 m) |
| ?? Apr 1951 | VRN | Veronique P2 | Technology | S |
| 02 Oct 1951 | SPS | Veronique R3 | Technology | S ? (15 m) |
| 05 Oct 1951 | SPS | Veronique R4 | Technology | S (1800 m) |
| 06 Oct 1951 | SPS | Veronique R5 | Technology | S (1820 m) |
| 25 Jan 1952 | CDT | Veronique P6/1 | Technology | S |
| 26 Jan 1952 | CDT | Veronique R7 | Technology | PS Nosecone not jettisoned |
| 28 Jan 1952 | CDT | Veronique P6/2 | Technology | S |
| 28 Jan 1952 | CDT | Veronique R6 | Technology | S (1100 m) |
| 30 Jan 1952 | CDT | Veronique R8 | Technology | S |
| Date | Site | Vehicle | Mission | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 May 1952 | HMG | Veronique N1 | Technology | F (19 km) |
| 21 May 1952 | HMG | Veronique N2 | Technology | F (14 km) |
| 22 May 1952 | HMG | Veronique N3 | Technology | S (60 km) |
| 08 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N4 | Technology | F (10 km) |
| 09 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N5 | Technology | F (<1 km) |
| 13 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N7 | Technology | F (4 km) |
| 16 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N6 | Technology | F (6 km) |
| 17 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N9 | Technology | F (10 km) |
| 18 Nov 1952 | HMG | Veronique N8 | Technology | F (7 km) |
| 18 Apr 1953 | HMG | Veronique N11 | Technology | F (3 km) |
| 21 Apr 1953 | HMG | Veronique N10 | Technology | S (45 km) |
| 20 Feb 1954 | HMG | Veronique NA15 | Technology | F (29 km) |
| 21 Feb 1954 | HMG | Veronique NA14 | Technology | S (135 km) |
| 17 Oct 1954 | HMG | Veronique NA13 | Technology | F (39 km) |
| 29 Oct 1954 | HMG | Veronique NA12 | VLF transmission | S (104 km) |
| 07 Mar 1959 | HMG | Veronique AGI18 | Na release | F |
| 10 Mar 1959 | HMG | Veronique AGI17 | Na release | S |
| 12 Mar 1959 | HMG | Veronique AGI16 | Na release | S |
| 23 Feb 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI23 | Scientific | F |
| 02 Mar 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI22 | Na release | S |
| 05 Mar 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI21 | Na release | S |
| 13 Jun 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI20 | Na release | S |
| 16 Jun 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI19 | Na release | S |
| 18 Jun 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI25 | Explosivee | S |
| 22 Jun 1960 | HMG | Veronique AGI26 | Explosive | S |
| 11 Feb 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI27 | Scientific | S |
| 13 Feb 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI28 | Scientific | F |
| 15 Feb 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI29 | Scientific | S |
| 18 Feb 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI30 | Scientific | F |
| 22 Feb 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI24 | Biology | S (110 km) |
| 10 Jun 1961 | HMG | Veronique AGI31 | Double explosive | S |
| 24 May 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI39 | Explosive | S (168 km) |
| 31 May 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI38 | Explosive | S |
| 01 Jun 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI41 | Double explosive | S |
| 04 Jun 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI42 | Double explosive | F |
| 06 Jun 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI43 | Explosive | S |
| 15 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI37 | Biology | S (120 km) |
| 18 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI36 | Biology | PS (110 lm) |
| 19 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI44 | Technology | S (135 km) |
| 22 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI46 | Technology | S (120 km) |
| 23 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI32 | Diffuse solar radiation | S (175 km) |
| 29 Oct 1962 | HMG | Veronique AGI34 | VLF transmission | S (180 km) |
| 20 Apr 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI35 | Ionosphere | S (175 km) |
| 23 Apr 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI49 | Ionosphere | S (140 km) |
| 01 May 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI45 | Ionosphere | S (160 km) |
| 10 May 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI33 | Solar corona (UV) / Ptr | PS (135 km), no recovery |
| 18 Jun 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI48 | Electron density | PS (160 km) |
| 19 Jun 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI40 | Electron density | VF (38 km), Destroyed at 34 sec |
| 18 Oct 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI47 | Biology | S (155 km) |
| 24 Oct 1963 | HMG | Veronique AGI50 | Biology | F (88 km) |
| 14 Apr 1964 | HMG | Veronique AGI51 | FU110 Atomic H (Ly-alpha), Solar X-rays | PS (119 km) |
| 08 Jun 1964 | HMG | Veronique 61/75 | FU120 Technology | S (260 km) |
| 13 Jun 1964 | HMG | Veronique 61/76 | FU120 Technology | S (260 km) |
| 04 Nov 1964 | HMG | Veronique AGI53 | FU110 Atomic H (Ly-alpha), Solar X-rays | S (152 km) |
| 08 Nov 1964 | HMG | Veronique AGI52 | FU111 UV Solar Astronomy / Ptr | S (98 km) |
| 12 Feb 1965 | HMG | Veronique AGI56 | FU100 Technology / Ptr | F (95 km), untimely fairing jettison |
| 27 May 1965 | HMG | Veronique 61/79 | FU144 Atomic H (Ly-alpha) | VF (70 km) |
| 22 Oct 1965 | HMG | Veronique AGI54 | FU115 Electron density | S (210 km) |
| 28 Oct 1965 | HMG | Veronique AGI55 | FU115 Electron density | S (210 km) |
| 24 Mar 1966 | HMG | Veronique 61M/80 | FU155 Technology | S (209 km) |
| 04 Apr 1966 | HMG | Veronique 61M/78 | FU145 Technology (Attitude control) | VF (23 km) |
| 06 Apr 1966 | HMG | Veronique AGI57 | FU126 Solar corona (UV) / Ptr | S (130 km) |
| 27 Jun 1966 | HMG | Veronique AGI60 | FU154 Technology (recovery) | S (123 km) |
| 01 Oct 1966 | HMG | Veronique 61M/77 | FU145 Technology + Ionosphere / Stab | PS (166 km) |
| 24 Nov 1966 | HMG | Veronique 61M/82 | FU158 Technology (recovery) | PS (230 km) |
| 09 Dec 1966 | HMG | Veronique AGI59 | FU149 Ion Density, mass spectrometry | S (122 km) |
| 11 Jan 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/84 | FU161 X-ray and UV astronomy / Stab | S (158 km) |
| 13 Jan 1967 | HMG | Veronique AGI61 | FU160 Solar corona (UV) / Ptr | S (123 km) |
| 17 Jan 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/85 | FU145b X-ray and UV astronomy / Stab | S (205 km) |
| 24 Feb 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/81 | FU176 Technology (recovery) | S (200 km) |
| 17 Mar 1967 | HMG | Veronique AGI64 | FU174 Solar corona (UV) / Ptr | VF (32 km) |
| 24 Mar 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/86 | FU156 Ionosphere + Biology | S (365 km) |
| 29 Mar 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/87 | FU156 Ionosphere + Biology | S (305 km) |
| 04 Apr 1967 | HMG | Veronique 61M/88 | FU178 X-ray and UV astronomy / Stab | S (196 km) |
| 09 Apr 1968 | KRU | Veronique AGI62 | FU184 Technology (sea recovery) | S (113 km) |
| 25 Jul 1968 | KRU | Veronique 61M/89 | FU185 Technology + X-ray astronomy / Stab | PS (185 km), no recovery |
| 18 Dec 1968 | KRU | Veronique 61M/83 | FU159 UV astronomy / Stab | PS (162 km), no recovery |
| 22 Dec 1968 | KRU | Veronique 61M/90 | FU159 X-ray and UV astronomy / Stab | PS (188 km), no recovery |
| 20 Feb 1969 | KRU | Veronique AGI63 | FU170 CIRCE, Mass spectrometry | F (103 km), untimely fairing jettison |
| 08 Jun 1971 | KRU | Veronique 61M/93 | FU194 GESAIR, Ionosphere + Biology | S (206 km) |
| 12 Jun 1971 | KRU | Veronique 61M/94 | FU194 GESAIR, Ionosphere + Biology | S (211 km) |
| 16 Dec 1971 | KRU | Veronique 61M/92 | FU208 CISASPE, Ionosphere (active sounding) | S (227 km) |
| 17 Apr 1973 | KRU | Veronique 61M/ | FU200 3SUV, UV solar astronomy / Ptr | S (200 km) |
| 31 May 1975 | KRU | Veronique 61M/ | FU216 FAUST, UV astronomy / Stab | SF (172 km) |
| Date | Site | Vehicle | Mission | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 Oct 1965 | HMG | Vesta 01 | FU123 Technology | S (187 km) |
| 25 Oct 1965 | HMG | Vesta 02 | FU123 Technology | S (109 km) |
| 07 Mar 1967 | HMG | Vesta 04 | FU147 Biology | S (243 km) |
| 13 Mar 1967 | HMG | Vesta 05 | FU147 Biology | S (234 km) |
| 08 Nov 1969 | KRU | Vesta 06 | FU189 Astronomy | S (204 km) |